In today’s diverse and interconnected world, ensuring inclusiveness in project activities is not only a moral imperative but also a practical necessity. Inclusiveness ensures that the benefits of a project reach all stakeholders, particularly marginalized and underrepresented groups. Project monitoring plays a critical role in assessing and ensuring this inclusiveness. This essay explores the importance of monitoring for inclusiveness, the challenges involved, and effective strategies for achieving truly inclusive project outcomes.
Inclusiveness in project implementation ensures that every voice is heard, every need is addressed, and every person is valued.
Importance of Inclusiveness in Project Activities
Inclusiveness in project activities ensures that all segments of the population, regardless of gender, age, ethnicity, disability, or socioeconomic status, have equitable access to the benefits and opportunities provided by the project. It fosters social cohesion, reduces inequalities, and enhances the overall effectiveness and sustainability of the project. Inclusive projects are more likely to gain widespread support, as they address the needs and aspirations of a broader spectrum of society.
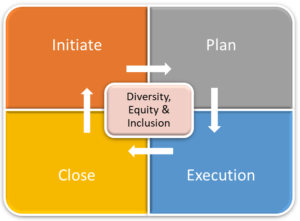
Role of Project Monitoring in Ensuring Inclusiveness
Project monitoring involves the continuous assessment of project activities to ensure that they are on track to achieve their objectives. In the context of inclusiveness, monitoring plays several key roles:
- Identifying Barriers: Monitoring helps identify barriers that prevent certain groups from participating in or benefiting from project activities. These barriers could be physical, social, economic, or cultural.
- Assessing Participation: It tracks the participation rates of different groups, ensuring that marginalized and underrepresented populations are actively involved in the project.
- Evaluating Impact: Monitoring evaluates the impact of project activities on various groups, ensuring that the benefits are equitably distributed and that no group is disproportionately affected negatively.
- Ensuring Accountability: Continuous monitoring ensures that project implementers are held accountable for maintaining inclusiveness throughout the project lifecycle.
- Facilitating Adaptive Management: It provides real-time data that can be used to make necessary adjustments to project activities to enhance inclusiveness.
Challenges in Monitoring for Inclusiveness
- Data Collection: Collecting disaggregated data by gender, age, ethnicity, disability, and other factors can be challenging, especially in contexts where such data is not readily available or culturally sensitive.
- Resource Constraints: Adequate monitoring requires resources such as trained personnel, funding, and time, which may be limited in some projects.
- Bias and Assumptions: Monitoring processes can be influenced by biases and assumptions, leading to inaccurate assessments of inclusiveness.
- Complexity of Inclusiveness: Inclusiveness is a multi-dimensional concept that involves various intersecting factors, making it difficult to monitor comprehensively.
Strategies for Effective Monitoring of Inclusiveness
- Develop Inclusive Indicators: Create specific, measurable indicators that reflect the inclusiveness of project activities. These indicators should cover various dimensions such as participation rates, access to resources, and impact on different groups.
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve representatives from marginalized and underrepresented groups in the design, implementation, and monitoring of the project. Their insights can help identify relevant indicators and potential barriers to inclusiveness.
- Use Mixed Methods: Employ both quantitative and qualitative methods to capture a comprehensive picture of inclusiveness. Surveys, focus group discussions, and participatory assessments can provide valuable data.
- Ensure Disaggregated Data: Collect and analyze data disaggregated by key factors such as gender, age, ethnicity, and disability. This helps in identifying disparities and tailoring interventions accordingly.
- Build Capacity: Train project staff and stakeholders in inclusive monitoring practices. This includes understanding the importance of inclusiveness, data collection techniques, and analysis.
- Implement Feedback Mechanisms: Establish feedback mechanisms that allow beneficiaries to voice their concerns and experiences. This can help identify areas where inclusiveness needs improvement.
- Regular Reviews and Adjustments: Conduct regular reviews of the monitoring data to assess progress and make necessary adjustments to the project activities to enhance inclusiveness.
Conclusion
Ensuring inclusiveness in project activities is essential for achieving equitable and sustainable development outcomes. Project monitoring plays a crucial role in assessing and promoting inclusiveness by identifying barriers, tracking participation, evaluating impacts, ensuring accountability, and facilitating adaptive management. Despite the challenges, effective strategies such as developing inclusive indicators, engaging stakeholders, using mixed methods, ensuring disaggregated data, building capacity, implementing feedback mechanisms, and conducting regular reviews can significantly enhance the inclusiveness of project activities. By prioritizing inclusiveness, projects can better address the needs of all stakeholders and contribute to a more just and equitable society.